-
Energy consumption
- Coût du kwh électrique
- Energy production
- Energy consumption
- Worldwide energy resources
- The sustainable development
- Energy and its various forms
- Conversion of energy forms
- Efficiency of processus
- Green energy plants
- Force conservative et énergie
- Over-unity and conversion process
- Amplify the inlet energy
- Modes de production d'énergie
- Production d'énergie et pollution
- Edition
-
Energy consumption
Worldwide energy consumption
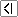
The world's energy consumption is almost exclusively a carbon based energy.
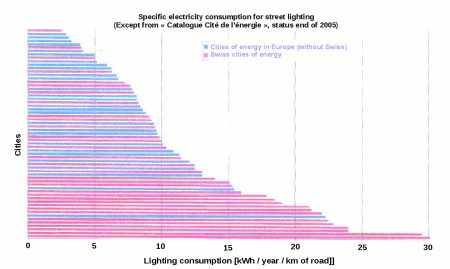
Lighting of streets and buildings in cities
Economic issues energy, climate change
The lighting is a prime area for cost savings, because the waste is enormous. Without compromising its mission, best practices, combined with technological advances, make a deposit of potentially significant savings of greenhouse gas emissions in a more and more carboned European electricity market.
A better understanding of lighting points park, a better fit subscription and purchased power, a reduction of lamp power, allow substantial budgetary savings.
But beyond the simple question of tariff, the current standard of illumination are equal to or greater than 15 MWh / year / km of road.
While the target set by the European Energy Award (EEA), presented at the European level, is 5 MWh / year / km of road.
The potential savings in France are therefore particularly important.
The issue of sufficient power to fulfill a given mission must be asked. Extremely harmful to the environment, the criteria for uniformity of illumination should be of the utmost restraint. Minimizing overall impact passes through reduced light power (lumen) compared to current practice, but not limited only to the energy consumption (in watts).
The public lighting in France
- About 2 nuclear reactors of 1000 megawatt.
- 18% of the energy consumption of local communities.
- Average lamp power: 180 W.
- Evolution from 70 to 91 kWh / year / inhabitant over 10 years (Germany: 43 kWh / year / capita).
- 30% of luminous points over 10 years.
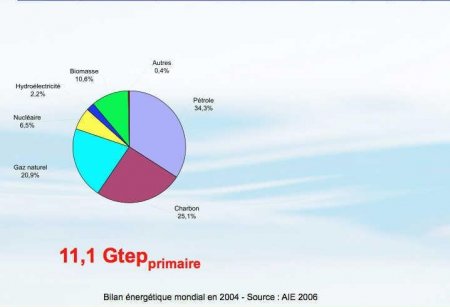
- Evolution of the illumination time over 10 years, growing to 4000 hours / year
Energy consumption of European cities for lighting of street